
Table of Contents
As a publisher, author or content creator, the time may come to expand to other markets. Does that really mean a full textbook translation is necessary? Most likely, the answer is yes.
In this comprehensive guide to textbook translation in 2024, we’ll cover textbook translations as a whole, machine translation, other costs, timelines and why hiring freelancers is a risky choice. We also answer other key questions to help you make an informed decision on who to hire.
Textbook translations: a unique beast
Those who publish content in English often believe that translation is an unnecessary expense. On the contrary. Studies show that students generally comprehend academic materials better in their native languages (1). Not only that, but native-language materials often evoke a stronger emotional connection, as well (2). Plus, if you are a publisher offering an online content platform, localized material is often a key selling point.
Textbook translations are in a class of their own. Agencies or publishers must assemble a dedicated team of linguists who are trained specifically on the subject matter. Throughout the translation, the agency or publisher must exert strict oversight over this team (we examine these measures in our article, How to Manage a Textbook Translation).
The following factors contribute to the unique nature of textbook translations:
- Volume: In many cases, textbooks can span millions of words, requiring large-scale technological capabilities and complex planning. Agencies or publishers must tie together a range of disparate subjects and make each chapter sound like it was written by a single person.
- Use as reference: Students pore over chapters and can read them in minute detail, over and over. This leaves the translation open to increased scrutiny. For this reason, it is imperative that the content also be perceived as reliable. One inconsistent term or grammar error in a textbook translation can undermine the authority of the entire text.
- Specialized terminology: Textbooks often contain subject-specific terminology that requires specialized knowledge to translate. A translator without expertise in the textbook’s subject could mistranslate key terms, leading to confusion or misinformation.
- Cultural sensitivity: Educational materials must resonate with the target audience’s cultural and educational norms. A good textbook translation isn’t just about converting words from one language to another—it’s about adapting the content so it is meaningful and relevant to the students in the target market.
- Complex formatting: Print textbooks are often written in specialized software that requires some sort of conversion to reach editable format. Even if the text is fully online (in an xml format, for example), it still contains graphs, tables, diagrams and references, which in many cases must be converted into editable format, requiring the use of third-party providers. Then, they must all be formatted correctly and translated while referencing the body text. This requires a higher level of technical proficiency than what is required for simpler documents like blog posts, marketing materials or even legal documents.
Machine translation as a cost-saving measure
In 2024, textbook publishers are increasingly turning to new technologies like machine translation (MT) to cut costs and save time. To give you an idea, MT can reduce the cost of translation by up to 30%–40%. Nonetheless, these advancements are not a complete solution on their own.
While the MT engine can quickly generate translations, the output is often riddled with errors in syntax, terminology and style. It lacks the nuanced understanding required for educational materials and complex subject matter. It is also extremely inconsistent—MT often translates key terms differently throughout the text, even if the context is identical.
Machine translation post-editing
Professional human translators must step in to correct the machine-generated content, in a process called machine translation post-editing (MTPE). The linguists edit the text and ensure it complies with the style guide, glossary and cultural requirements, among others.
All first-rate translation agencies in 2024 offer MTPE services and maintain relationships with linguists specialized in MTPE. This is why tight collaboration between textbook publishers and specialized translation agencies is crucial. By combining the efficiency of MT with the expertise of professional translators and project managers, publishers can achieve accurate, high-quality translations while keeping costs manageable.
Get your textbook translation moving.
Textbook translations don’t have to be daunting. Plan the best way forward.
Pricing and extra costs
Understanding how agencies price their services and anticipating potential extra costs is crucial. Pricing structures can vary based on several factors, but agencies typically use transparent systems that help clients gauge the overall cost before the project begins.
Per-word pricing
The most common method for pricing textbook translations is per word. The cost per word varies depending on several factors, including:
- Language pair: Common languages (e.g., Spanish or French) generally cost less, while rare or more complex languages (e.g., Mandarin or Arabic) may have higher per-word rates.
- Complexity of content: Textbooks that require subject matter expertise (e.g., medical, technical, or scientific content) typically command a higher per-word rate due to the specialized knowledge needed.
- Translation quality and services: Some agencies offer different tiers of service. For example, basic translation may cost less, but full-service translation— which includes editing, proofreading and quality assurance—will raise the price. Note: Boutique Translations never charges extra for QA.
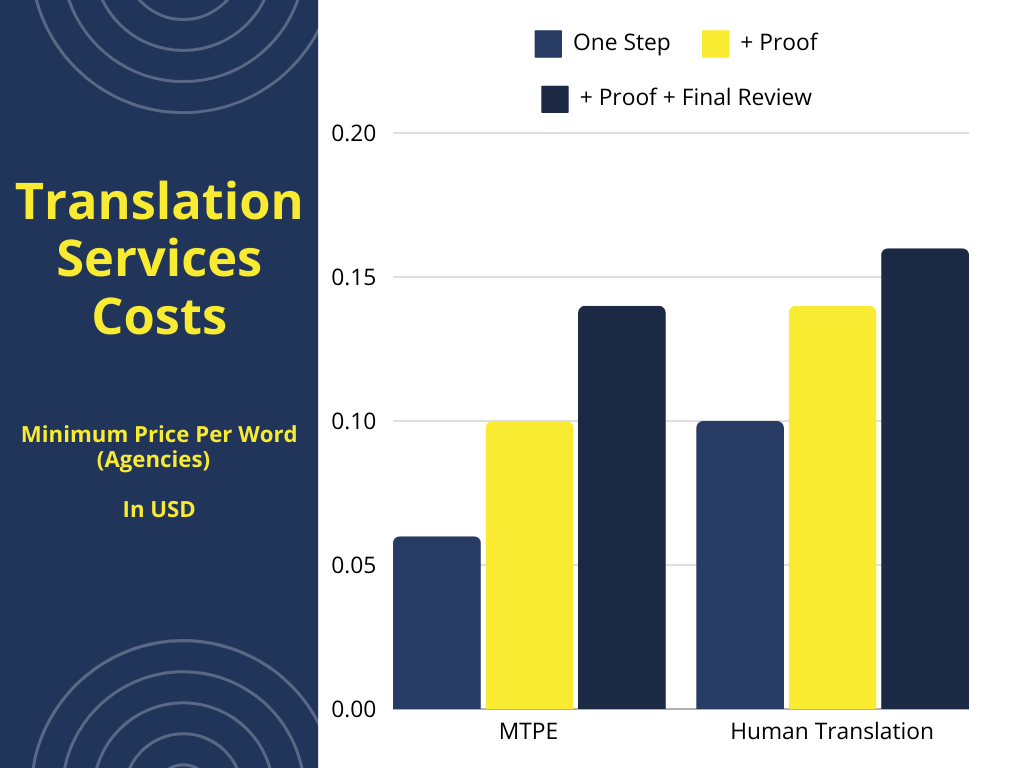
Per-word rates for full translation (without proofreading) range from $0.10 to $0.25 for standard languages and $0.25 to $0.50 for more technical or rare languages. Expect to pay less if you are requesting MTPE with no proofreading step.
Per-page pricing
For textbooks with a high concentration of visuals, charts and complex layouts, some agencies may prefer to charge per page. This method accounts for both the volume of text and the intricacies of formatting and layout.
Per-page rates can range from $20 to $50 depending on the textbook’s complexity and content density.
Hourly rates
In some cases, agencies may charge hourly for specific tasks such as desktop publishing (DTP) or localization of images, diagrams and interactive content. Hourly rates may also apply for services like glossary creation or terminology management.
Hourly rates can range from $30 to $100, depending on the region and the expertise required for the task.
Flat project fee
For large-scale textbook projects, agencies sometimes offer a flat project fee. This pricing model provides a clear estimate from the beginning, allowing clients to budget more accurately. The flat fee is calculated based on the estimated total word count, the complexity of the content and any additional services requested (such as proofreading or layout adjustments). This can be particularly helpful for multi-volume or series-based textbooks.
Extra costs
In addition to standard translation costs, textbook translation projects often entail extra expenses. These could include:
File conversion
Textbooks are often created in specialized software such as Adobe Indesign, QuarkXPress, Scribus, FrameMaker, or even LaTeX. CAT tools are not capabable of editing these files directly. Thus, they must be converted into editable format and then converted back into the original file type.
File conversion is usually charged by hour and can range from $30 to $100 per hour.
Desktop publishing and formatting
Textbooks typically contain charts, tables, graphs, diagrams and other complex formatting that must be preserved or adapted during the translation process. This often requires specialized desktop publishing (DTP) services to ensure the translated content fits properly within the original layout and maintains readability. Additionally, textbooks with highly technical illustrations or interactive elements may need adjustments to make sure they remain functional and relevant in the target language.
DTP costs can range from $5 to $30 per page, depending on the complexity of the layout.
Glossary creation and terminology management
If the textbook contains specialized terminology, agencies may offer terminology management services, including creating or adapting glossaries to ensure consistent use of terms throughout the translation. This is particularly important for educational materials that need to align with a specific curriculum or educational standard.
Glossary creation can be charged as a flat fee or on an hourly basis and depends greatly on the scope and number of terms. Note: Boutique Translations does not charge extra for terminology management once the glossary has been created.
Rush fees
If you need the translation completed within a tight deadline, agencies often charge rush fees to prioritize your project. Expediting the process requires additional resources and could mean working with a larger team of translators to meet deadlines, which increases the overall cost.
Rush fees typically range from 20% to 50% more than standard rates, depending on the urgency and project complexity.
Legal or regulatory compliance
For educational materials that need to comply with specific legal or educational standards (especially for government contracts or international use), additional costs may arise from ensuring the textbook adheres to these standards. This could involve working with local educational consultants or legal experts.
Compliance costs vary significantly depending on the region and type of compliance needed, but can range from $500 to several thousand dollars.

Should I hire freelancers or a translation agency?
One of the most critical decisions when planning your textbook translation project is whether to hire individual freelancers or a specialized translation agency. While freelancers may seem like a cost-effective option, there are several reasons why they may not be suitable for large-scale textbook translation projects.
1. Freelancers lack project management support:
One of the major advantages of hiring a specialized textbook translation agency is the robust project management they provide. Textbook translation projects are complex, involving multiple stages such as translation, proofreading, editing and formatting. A professional agency will assign a dedicated project manager to oversee the entire process, ensuring that the project runs smoothly and meets deadlines.
Freelancers, on the other hand, often work independently and may lack the resources or experience to manage a large-scale project. You may end up having to manage multiple freelancers, which can lead to communication breakdowns, inconsistencies in the translation and missed deadlines.
2. Quality control is stronger with agencies:
A specialized translation agency employs rigorous quality assurance processes, including multiple rounds of proofreading and editing. They may also use specialized tools such as translation memory software to ensure consistency throughout the project. Freelancers, however, may not have access to these resources or be able to provide the same level of quality control.
3. Freelancers may lack specialized expertise:
Freelancers often generalize in many areas and while they may be skilled at general translation tasks, they may lack the specialized expertise required for translating textbooks in specific subject areas. An agency, on the other hand, can assemble a team of subject matter experts who are familiar with the terminology and nuances of the textbook’s topic.
4. Freelancers may not handle volume efficiently:
Textbooks are usually large, multi-chaptered projects that require a lot of time and effort to translate. Freelancers may not have the capacity to handle such large volumes of work, which could result in missed deadlines and rushed work. Agencies, with their larger teams and better infrastructure, are better equipped to handle these large projects efficiently.
5. Legal and Contractual Protections:
A professional translation agency typically operates under legal contracts that protect both parties. If there are any disputes or issues with the translation, the agency is bound to fix these under the agreed terms. Freelancers, particularly those working without contracts, may not offer the same level of legal protection or accountability.
What to Keep in Mind if you Do Hire Freelancers
If you want to launch an MTPE project and decide to send your textbook to one or more freelancers, make sure they are trained in MTPE. Not all linguists can handle post-editing machine translations, as MTPE requires specific skills and training to do it effectively. Here’s why:
- Understanding MT Limitations: Linguists trained in MTPE understand the MT engine’s strengths and common errors, allowing them to quickly identify and correct errors that a less experienced translator might overlook.
- Expertise in CAT Tools: Computer-Assisted Translation (CAT) tools, such as Trados, memoQ and Smartcat, are essential for managing MTPE projects efficiently. These tools integrate machine translation engines and enable linguists to streamline the post-editing process.
- Terminology Management: In specialized fields like education, medicine or engineering, textbook translations demand precise use of terminology. This is where linguists’ glossary management knowledge comes into play.
- QA Processes: Trained MTPE linguists know how to conduct in-depth quality assurance (QA) checks to ensure that the translation is culturally appropriate, contextually accurate and aligned with the glossary.
- Speed Without Compromising Quality: MTPE requires a balance of speed and precision. Trained linguists are able to quickly navigate through machine-generated text, making necessary corrections without sacrificing quality.
If you still decide to award your project to a single freelancer, taking all of these factors into account, I sincerely tip my hat to that person. They must really have a great profile!
Conclusion: Investing in professional textbook translation in 2024

Translating textbooks requires much more than just converting words from one language to another. With advancements in technology like machine translation and the growing complexity of educational content, it’s crucial to partner with a specialized textbook translation agency that understands the unique demands of these projects. From accurate terminology and subject matter expertise to handling complex layouts and ensuring cultural appropriateness, a professional agency brings the expertise, project management and quality assurance necessary to deliver a polished final product.
While the price of textbook translation may seem high, especially when compared to freelancers or simple machine translation, the investment in a specialized agency ensures that the translation is accurate, consistent and aligned with the educational standards required for your audience. MTPE can offer cost-saving benefits, but only when handled by trained professionals using the appropriate tools.
By choosing an experienced textbook translation agency, you’ll not only receive high-quality translations but also avoid common pitfalls, such as delayed delivery, inconsistencies, or legal issues. In the end, investing in professional textbook translation ensures that your educational materials are effectively translated and accessible to a global audience, helping students worldwide to engage with the content in their native language.
Collaborate with an agency you can trust.
We put in the work to make your project rock solid, on budget.


0 Comments